# d3-ease
*Easing* is a method of distorting time to control apparent motion in animation. It is most commonly used for [slow-in, slow-out](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/12_basic_principles_of_animation#Slow_In_and_Slow_Out). By easing time, [animated transitions](https://github.com/d3/d3-transition) are smoother and exhibit more plausible motion.
The easing types in this module implement the [ease method](#ease_ease), which takes a normalized time *t* and returns the corresponding “eased” time *tʹ*. Both the normalized time and the eased time are typically in the range [0,1], where 0 represents the start of the animation and 1 represents the end; some easing types, such as [elastic](#easeElastic), may return eased times slightly outside this range. A good easing type should return 0 if *t* = 0 and 1 if *t* = 1. See the [easing explorer](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing) for a visual demonstration.
These easing types are largely based on work by [Robert Penner](http://robertpenner.com/easing/).
## Installing
If you use npm, `npm install d3-ease`. You can also download the [latest release on GitHub](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/releases/latest). For vanilla HTML in modern browsers, import d3-ease from Skypack:
```html
```
For legacy environments, you can load d3-ease’s UMD bundle from an npm-based CDN such as jsDelivr; a `d3` global is exported:
```html
```
[Try d3-ease in your browser.](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing-animations)
## API Reference
# ease(t)
Given the specified normalized time *t*, typically in the range [0,1], returns the “eased” time *tʹ*, also typically in [0,1]. 0 represents the start of the animation and 1 represents the end. A good implementation returns 0 if *t* = 0 and 1 if *t* = 1. See the [easing explorer](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing) for a visual demonstration. For example, to apply [cubic](#easeCubic) easing:
```js
const te = d3.easeCubic(t);
```
Similarly, to apply custom [elastic](#easeElastic) easing:
```js
// Before the animation starts, create your easing function.
const customElastic = d3.easeElastic.period(0.4);
// During the animation, apply the easing function.
const te = customElastic(t);
```
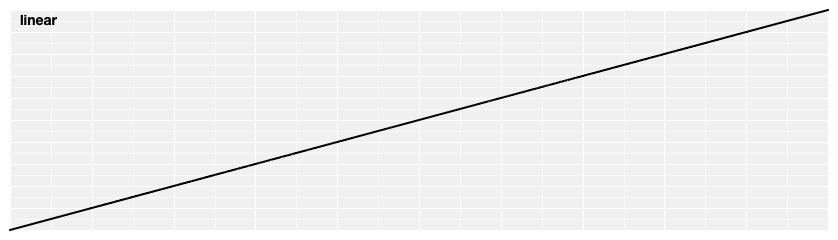
# d3.easeLinear(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/linear.js "Source")
Linear easing; the identity function; *linear*(*t*) returns *t*.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#linear)
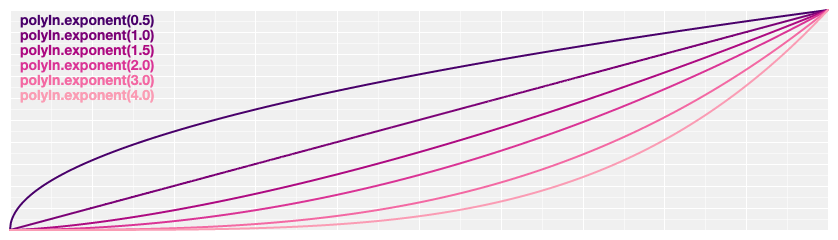
# d3.easePolyIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L3 "Source")
Polynomial easing; raises *t* to the specified [exponent](#poly_exponent). If the exponent is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#linear)
# d3.easePolyIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L3 "Source")
Polynomial easing; raises *t* to the specified [exponent](#poly_exponent). If the exponent is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyIn)
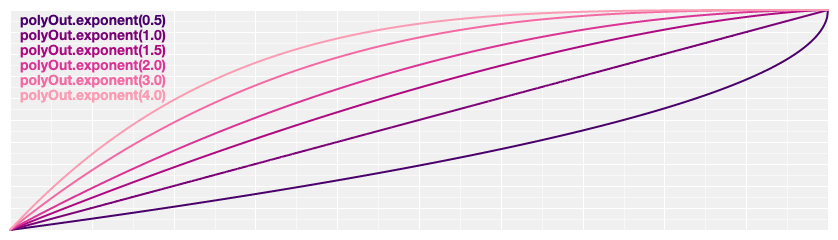
# d3.easePolyOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse polynomial easing; equivalent to 1 - [polyIn](#easePolyIn)(1 - *t*). If the [exponent](#poly_exponent) is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicOut](#easeCubicOut).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyIn)
# d3.easePolyOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse polynomial easing; equivalent to 1 - [polyIn](#easePolyIn)(1 - *t*). If the [exponent](#poly_exponent) is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicOut](#easeCubicOut).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyOut)
# d3.easePoly(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyOut)
# d3.easePoly(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js "Source")
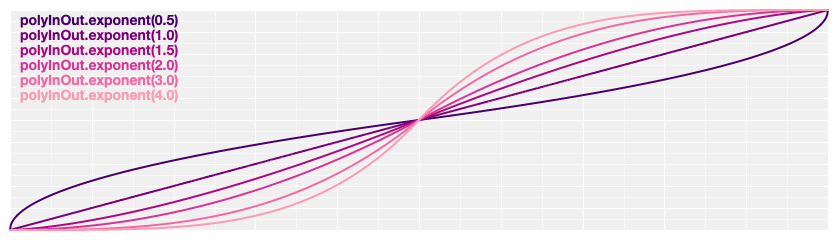
# d3.easePolyInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L27 "Source")
Symmetric polynomial easing; scales [polyIn](#easePolyIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [polyOut](#easePolyOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1]. If the [exponent](#poly_exponent) is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubic](#easeCubic).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyInOut)
# poly.exponent(e) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new polynomial easing with the specified exponent *e*. For example, to create equivalents of [linear](#easeLinear), [quad](#easeQuad), and [cubic](#easeCubic):
```js
const linear = d3.easePoly.exponent(1);
const quad = d3.easePoly.exponent(2);
const cubic = d3.easePoly.exponent(3);
```
# d3.easeQuadIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L1 "Source")
Quadratic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyInOut)
# poly.exponent(e) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new polynomial easing with the specified exponent *e*. For example, to create equivalents of [linear](#easeLinear), [quad](#easeQuad), and [cubic](#easeCubic):
```js
const linear = d3.easePoly.exponent(1);
const quad = d3.easePoly.exponent(2);
const cubic = d3.easePoly.exponent(3);
```
# d3.easeQuadIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L1 "Source")
Quadratic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[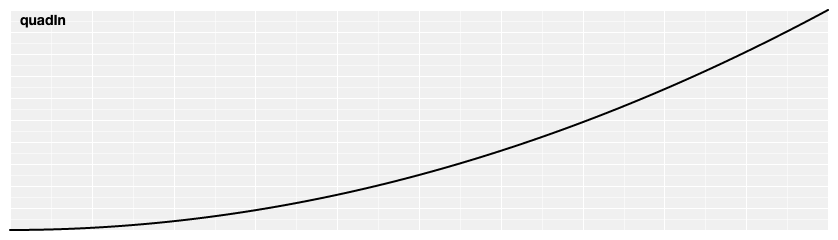 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadIn)
# d3.easeQuadOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse quadratic easing; equivalent to 1 - [quadIn](#easeQuadIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadIn)
# d3.easeQuadOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse quadratic easing; equivalent to 1 - [quadIn](#easeQuadIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[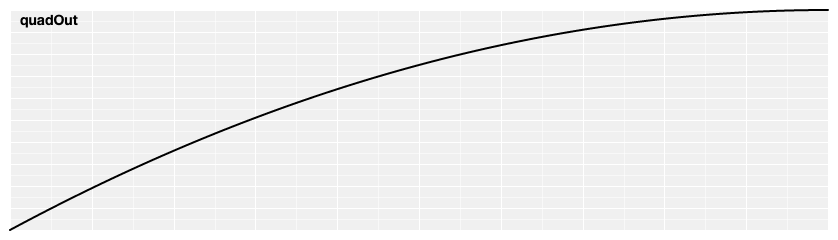 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadOut)
# d3.easeQuad(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadOut)
# d3.easeQuad(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js "Source")
# d3.easeQuadInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L9 "Source")
Symmetric quadratic easing; scales [quadIn](#easeQuadIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [quadOut](#easeQuadOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1]. Also equivalent to [poly](#easePoly).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[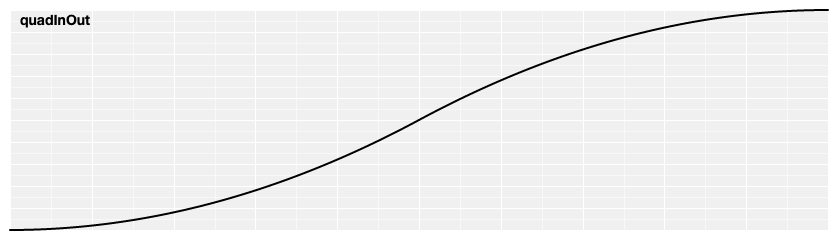 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadInOut)
# d3.easeCubicIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L1 "Source")
Cubic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadInOut)
# d3.easeCubicIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L1 "Source")
Cubic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[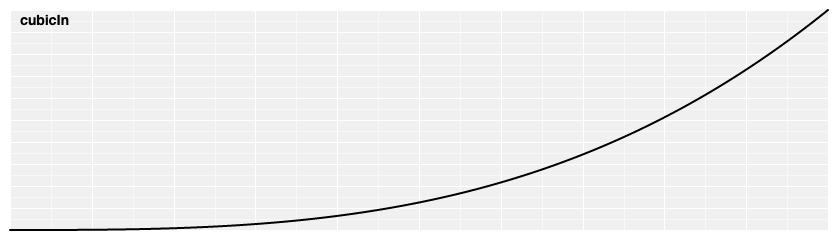 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicIn)
# d3.easeCubicOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse cubic easing; equivalent to 1 - [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicIn)
# d3.easeCubicOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse cubic easing; equivalent to 1 - [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[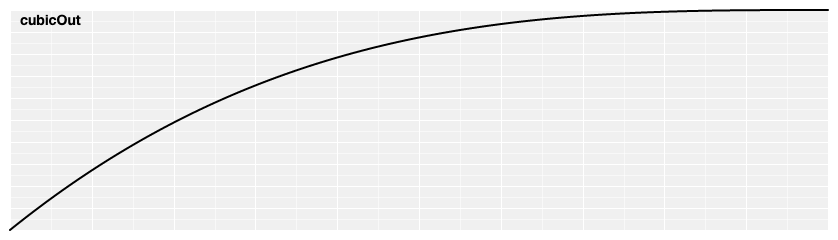 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicOut)
# d3.easeCubic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicOut)
# d3.easeCubic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js "Source")
# d3.easeCubicInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L9 "Source")
Symmetric cubic easing; scales [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [cubicOut](#easeCubicOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1]. Also equivalent to [poly](#easePoly).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[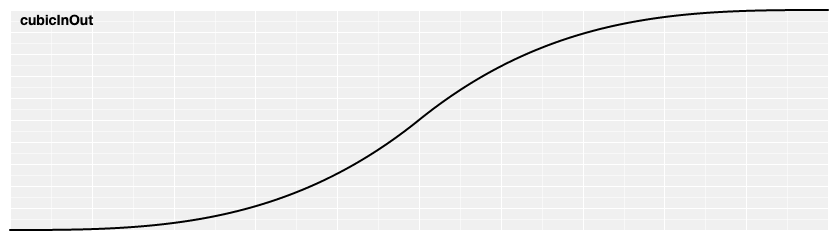 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicInOut)
# d3.easeSinIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L4 "Source")
Sinusoidal easing; returns sin(*t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicInOut)
# d3.easeSinIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L4 "Source")
Sinusoidal easing; returns sin(*t*).
[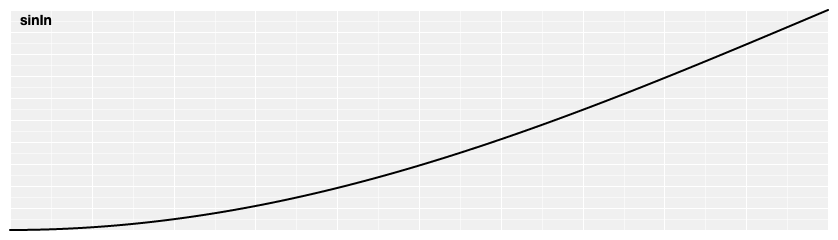 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinIn)
# d3.easeSinOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L8 "Source")
Reverse sinusoidal easing; equivalent to 1 - [sinIn](#easeSinIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinIn)
# d3.easeSinOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L8 "Source")
Reverse sinusoidal easing; equivalent to 1 - [sinIn](#easeSinIn)(1 - *t*).
[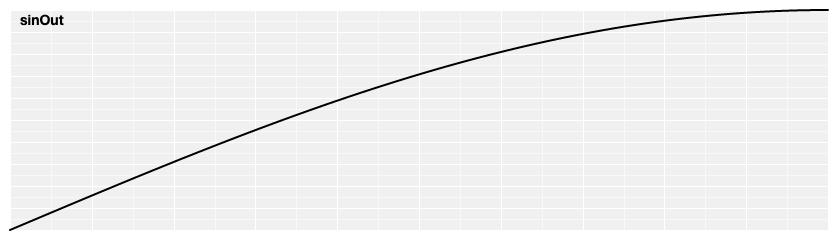 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinOut)
# d3.easeSin(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinOut)
# d3.easeSin(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js "Source")
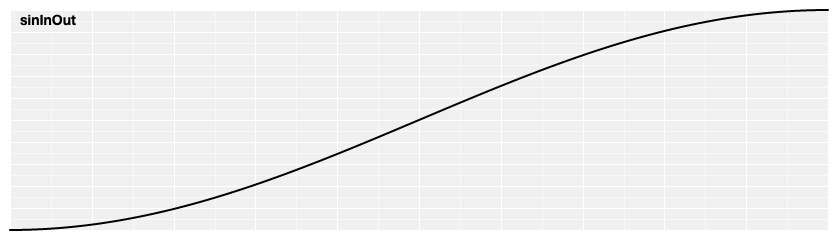
# d3.easeSinInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L12 "Source")
Symmetric sinusoidal easing; scales [sinIn](#easeSinIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [sinOut](#easeSinOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinInOut)
# d3.easeExpIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L1 "Source")
Exponential easing; raises 2 to the exponent 10 \* (*t* - 1).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinInOut)
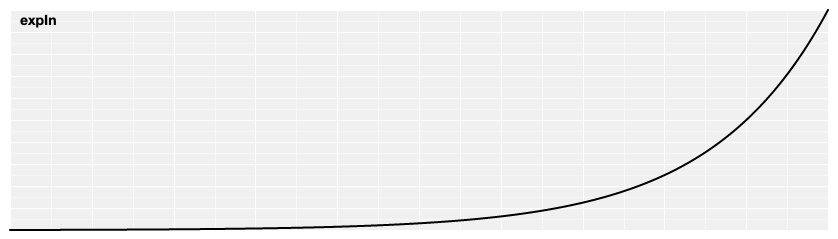
# d3.easeExpIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L1 "Source")
Exponential easing; raises 2 to the exponent 10 \* (*t* - 1).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expIn)
# d3.easeExpOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse exponential easing; equivalent to 1 - [expIn](#easeExpIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expIn)
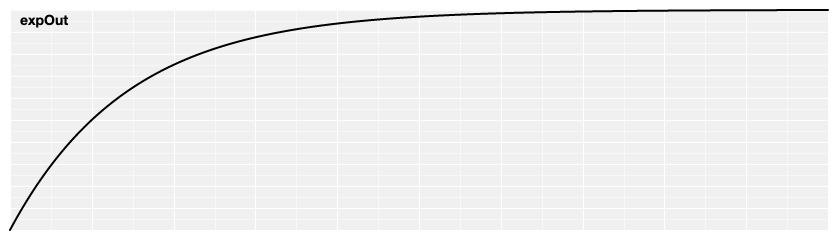
# d3.easeExpOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse exponential easing; equivalent to 1 - [expIn](#easeExpIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expOut)
# d3.easeExp(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expOut)
# d3.easeExp(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js "Source")
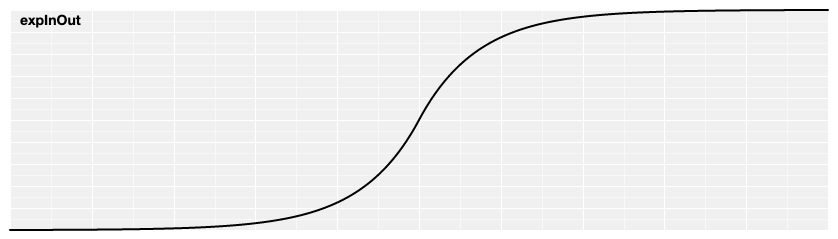
# d3.easeExpInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L9 "Source")
Symmetric exponential easing; scales [expIn](#easeExpIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [expOut](#easeExpOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expInOut)
# d3.easeCircleIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L1 "Source")
Circular easing.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expInOut)
# d3.easeCircleIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L1 "Source")
Circular easing.
[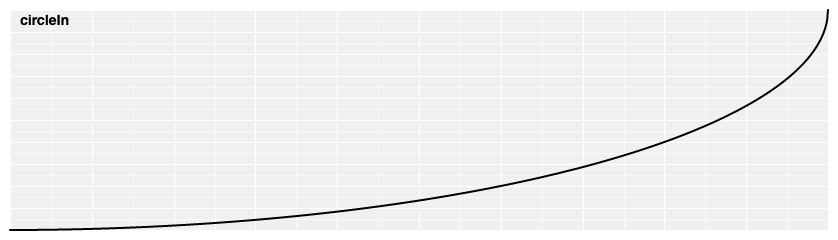 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleIn)
# d3.easeCircleOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse circular easing; equivalent to 1 - [circleIn](#easeCircleIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleIn)
# d3.easeCircleOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse circular easing; equivalent to 1 - [circleIn](#easeCircleIn)(1 - *t*).
[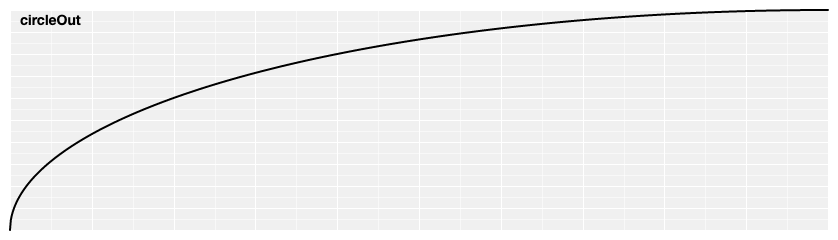 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleOut)
# d3.easeCircle(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleOut)
# d3.easeCircle(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js "Source")
# d3.easeCircleInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L9 "Source")
Symmetric circular easing; scales [circleIn](#easeCircleIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [circleOut](#easeCircleOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[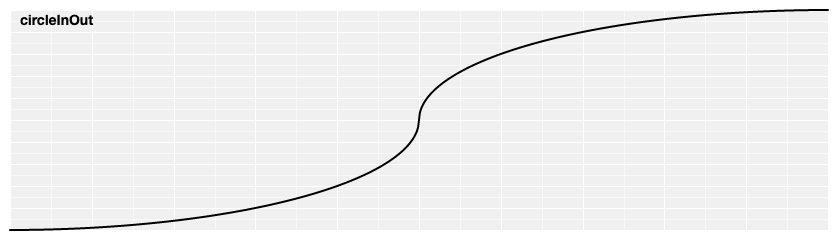 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleInOut)
# d3.easeElasticIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L5 "Source")
Elastic easing, like a rubber band. The [amplitude](#elastic_amplitude) and [period](#elastic_period) of the oscillation are configurable; if not specified, they default to 1 and 0.3, respectively.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleInOut)
# d3.easeElasticIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L5 "Source")
Elastic easing, like a rubber band. The [amplitude](#elastic_amplitude) and [period](#elastic_period) of the oscillation are configurable; if not specified, they default to 1 and 0.3, respectively.
[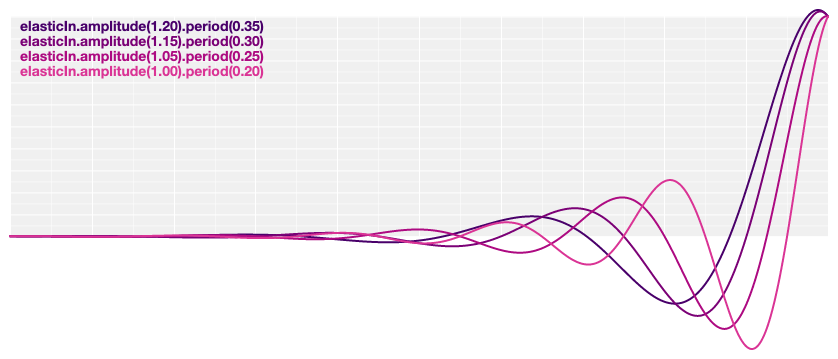 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticIn)
# d3.easeElastic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticIn)
# d3.easeElastic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js "Source")
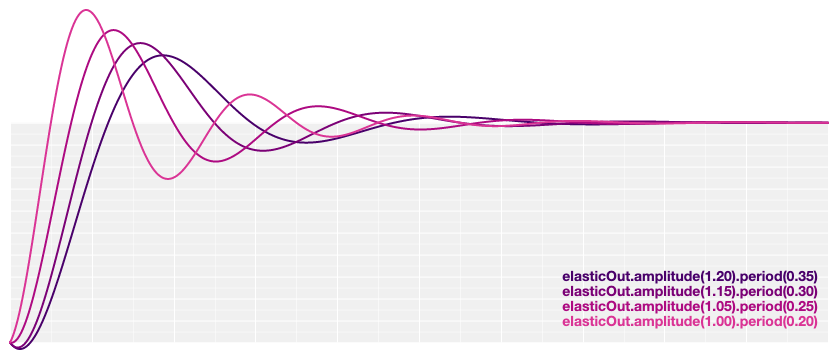
# d3.easeElasticOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L18 "Source")
Reverse elastic easing; equivalent to 1 - [elasticIn](#easeElasticIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticOut)
# d3.easeElasticInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L31 "Source")
Symmetric elastic easing; scales [elasticIn](#easeElasticIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [elasticOut](#easeElasticOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticOut)
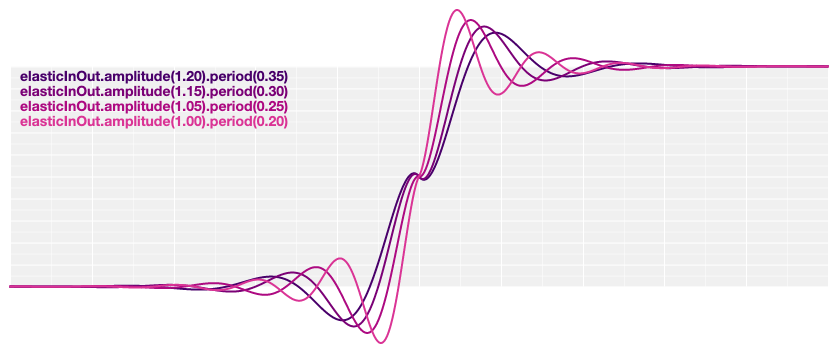
# d3.easeElasticInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L31 "Source")
Symmetric elastic easing; scales [elasticIn](#easeElasticIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [elasticOut](#easeElasticOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticInOut)
# elastic.amplitude(a) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L40 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified amplitude *a*.
# elastic.period(p) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L41 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified period *p*.
# d3.easeBackIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L3 "Source")
[Anticipatory](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/12_basic_principles_of_animation#Anticipation) easing, like a dancer bending his knees before jumping off the floor. The degree of [overshoot](#back_overshoot) is configurable; if not specified, it defaults to 1.70158.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticInOut)
# elastic.amplitude(a) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L40 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified amplitude *a*.
# elastic.period(p) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L41 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified period *p*.
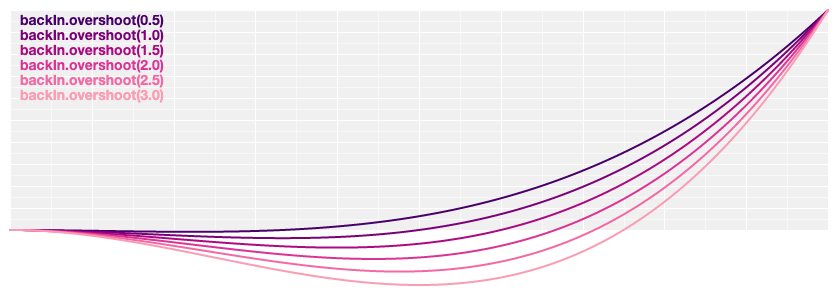
# d3.easeBackIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L3 "Source")
[Anticipatory](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/12_basic_principles_of_animation#Anticipation) easing, like a dancer bending his knees before jumping off the floor. The degree of [overshoot](#back_overshoot) is configurable; if not specified, it defaults to 1.70158.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backIn)
# d3.easeBackOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse anticipatory easing; equivalent to 1 - [backIn](#easeBackIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backIn)
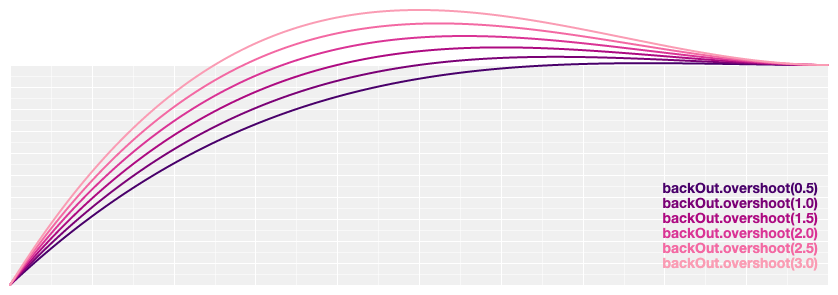
# d3.easeBackOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse anticipatory easing; equivalent to 1 - [backIn](#easeBackIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backOut)
# d3.easeBack(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backOut)
# d3.easeBack(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js "Source")
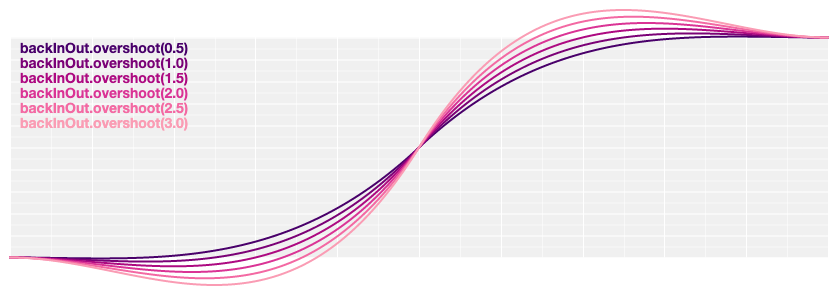
# d3.easeBackInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L27 "Source")
Symmetric anticipatory easing; scales [backIn](#easeBackIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [backOut](#easeBackOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backInOut)
# back.overshoot(s) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new back easing with the specified overshoot *s*.
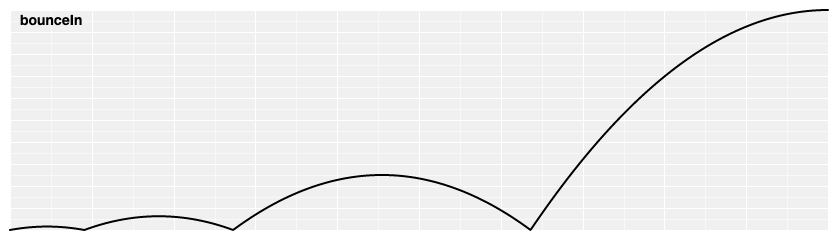
# d3.easeBounceIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L12 "Source")
Bounce easing, like a rubber ball.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backInOut)
# back.overshoot(s) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new back easing with the specified overshoot *s*.
# d3.easeBounceIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L12 "Source")
Bounce easing, like a rubber ball.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceIn)
# d3.easeBounce(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceIn)
# d3.easeBounce(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js "Source")
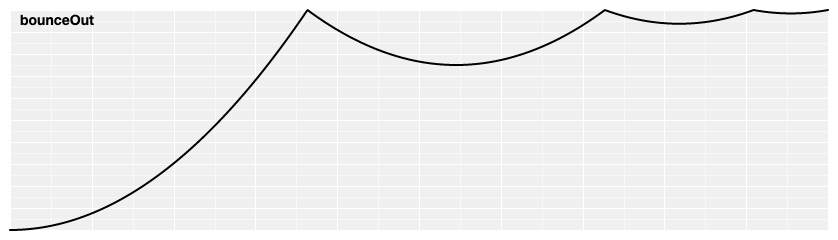
# d3.easeBounceOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L16 "Source")
Reverse bounce easing; equivalent to 1 - [bounceIn](#easeBounceIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceOut)
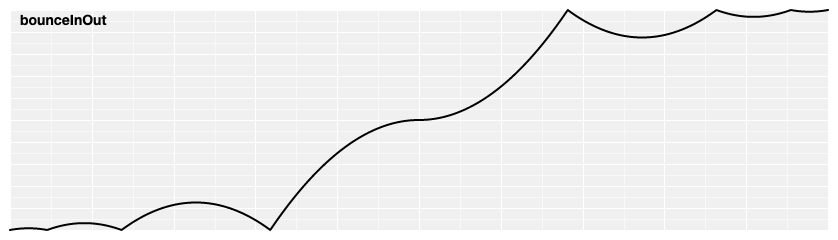
# d3.easeBounceInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L20 "Source")
Symmetric bounce easing; scales [bounceIn](#easeBounceIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [bounceOut](#easeBounceOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceOut)
# d3.easeBounceInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L20 "Source")
Symmetric bounce easing; scales [bounceIn](#easeBounceIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [bounceOut](#easeBounceOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceInOut)
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceInOut)
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#linear)
# d3.easePolyIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L3 "Source")
Polynomial easing; raises *t* to the specified [exponent](#poly_exponent). If the exponent is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#linear)
# d3.easePolyIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L3 "Source")
Polynomial easing; raises *t* to the specified [exponent](#poly_exponent). If the exponent is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyIn)
# d3.easePolyOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse polynomial easing; equivalent to 1 - [polyIn](#easePolyIn)(1 - *t*). If the [exponent](#poly_exponent) is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicOut](#easeCubicOut).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyIn)
# d3.easePolyOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse polynomial easing; equivalent to 1 - [polyIn](#easePolyIn)(1 - *t*). If the [exponent](#poly_exponent) is not specified, it defaults to 3, equivalent to [cubicOut](#easeCubicOut).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyOut)
# d3.easePoly(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyOut)
# d3.easePoly(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyInOut)
# poly.exponent(e) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new polynomial easing with the specified exponent *e*. For example, to create equivalents of [linear](#easeLinear), [quad](#easeQuad), and [cubic](#easeCubic):
```js
const linear = d3.easePoly.exponent(1);
const quad = d3.easePoly.exponent(2);
const cubic = d3.easePoly.exponent(3);
```
# d3.easeQuadIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L1 "Source")
Quadratic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#polyInOut)
# poly.exponent(e) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/poly.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new polynomial easing with the specified exponent *e*. For example, to create equivalents of [linear](#easeLinear), [quad](#easeQuad), and [cubic](#easeCubic):
```js
const linear = d3.easePoly.exponent(1);
const quad = d3.easePoly.exponent(2);
const cubic = d3.easePoly.exponent(3);
```
# d3.easeQuadIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L1 "Source")
Quadratic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadIn)
# d3.easeQuadOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse quadratic easing; equivalent to 1 - [quadIn](#easeQuadIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadIn)
# d3.easeQuadOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse quadratic easing; equivalent to 1 - [quadIn](#easeQuadIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(2).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadOut)
# d3.easeQuad(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadOut)
# d3.easeQuad(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/quad.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadInOut)
# d3.easeCubicIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L1 "Source")
Cubic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#quadInOut)
# d3.easeCubicIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L1 "Source")
Cubic easing; equivalent to [polyIn](#easePolyIn).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicIn)
# d3.easeCubicOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse cubic easing; equivalent to 1 - [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicIn)
# d3.easeCubicOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse cubic easing; equivalent to 1 - [cubicIn](#easeCubicIn)(1 - *t*). Also equivalent to [polyOut](#easePolyOut).[exponent](#poly_exponent)(3).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicOut)
# d3.easeCubic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicOut)
# d3.easeCubic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/cubic.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicInOut)
# d3.easeSinIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L4 "Source")
Sinusoidal easing; returns sin(*t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#cubicInOut)
# d3.easeSinIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L4 "Source")
Sinusoidal easing; returns sin(*t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinIn)
# d3.easeSinOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L8 "Source")
Reverse sinusoidal easing; equivalent to 1 - [sinIn](#easeSinIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinIn)
# d3.easeSinOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js#L8 "Source")
Reverse sinusoidal easing; equivalent to 1 - [sinIn](#easeSinIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinOut)
# d3.easeSin(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinOut)
# d3.easeSin(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/sin.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinInOut)
# d3.easeExpIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L1 "Source")
Exponential easing; raises 2 to the exponent 10 \* (*t* - 1).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#sinInOut)
# d3.easeExpIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L1 "Source")
Exponential easing; raises 2 to the exponent 10 \* (*t* - 1).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expIn)
# d3.easeExpOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse exponential easing; equivalent to 1 - [expIn](#easeExpIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expIn)
# d3.easeExpOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse exponential easing; equivalent to 1 - [expIn](#easeExpIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expOut)
# d3.easeExp(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expOut)
# d3.easeExp(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/exp.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expInOut)
# d3.easeCircleIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L1 "Source")
Circular easing.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#expInOut)
# d3.easeCircleIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L1 "Source")
Circular easing.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleIn)
# d3.easeCircleOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse circular easing; equivalent to 1 - [circleIn](#easeCircleIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleIn)
# d3.easeCircleOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js#L5 "Source")
Reverse circular easing; equivalent to 1 - [circleIn](#easeCircleIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleOut)
# d3.easeCircle(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleOut)
# d3.easeCircle(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/circle.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleInOut)
# d3.easeElasticIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L5 "Source")
Elastic easing, like a rubber band. The [amplitude](#elastic_amplitude) and [period](#elastic_period) of the oscillation are configurable; if not specified, they default to 1 and 0.3, respectively.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#circleInOut)
# d3.easeElasticIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L5 "Source")
Elastic easing, like a rubber band. The [amplitude](#elastic_amplitude) and [period](#elastic_period) of the oscillation are configurable; if not specified, they default to 1 and 0.3, respectively.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticIn)
# d3.easeElastic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticIn)
# d3.easeElastic(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticOut)
# d3.easeElasticInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L31 "Source")
Symmetric elastic easing; scales [elasticIn](#easeElasticIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [elasticOut](#easeElasticOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticOut)
# d3.easeElasticInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L31 "Source")
Symmetric elastic easing; scales [elasticIn](#easeElasticIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [elasticOut](#easeElasticOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticInOut)
# elastic.amplitude(a) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L40 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified amplitude *a*.
# elastic.period(p) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L41 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified period *p*.
# d3.easeBackIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L3 "Source")
[Anticipatory](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/12_basic_principles_of_animation#Anticipation) easing, like a dancer bending his knees before jumping off the floor. The degree of [overshoot](#back_overshoot) is configurable; if not specified, it defaults to 1.70158.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#elasticInOut)
# elastic.amplitude(a) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L40 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified amplitude *a*.
# elastic.period(p) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/elastic.js#L41 "Source")
Returns a new elastic easing with the specified period *p*.
# d3.easeBackIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L3 "Source")
[Anticipatory](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/12_basic_principles_of_animation#Anticipation) easing, like a dancer bending his knees before jumping off the floor. The degree of [overshoot](#back_overshoot) is configurable; if not specified, it defaults to 1.70158.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backIn)
# d3.easeBackOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse anticipatory easing; equivalent to 1 - [backIn](#easeBackIn)(1 - *t*).
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backIn)
# d3.easeBackOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L15 "Source")
Reverse anticipatory easing; equivalent to 1 - [backIn](#easeBackIn)(1 - *t*).
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backOut)
# d3.easeBack(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backOut)
# d3.easeBack(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backInOut)
# back.overshoot(s) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new back easing with the specified overshoot *s*.
# d3.easeBounceIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L12 "Source")
Bounce easing, like a rubber ball.
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#backInOut)
# back.overshoot(s) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/back.js#L1 "Source")
Returns a new back easing with the specified overshoot *s*.
# d3.easeBounceIn(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L12 "Source")
Bounce easing, like a rubber ball.
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceIn)
# d3.easeBounce(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js "Source")
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceIn)
# d3.easeBounce(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js "Source")
 ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceOut)
# d3.easeBounceInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L20 "Source")
Symmetric bounce easing; scales [bounceIn](#easeBounceIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [bounceOut](#easeBounceOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceOut)
# d3.easeBounceInOut(t) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-ease/blob/master/src/bounce.js#L20 "Source")
Symmetric bounce easing; scales [bounceIn](#easeBounceIn) for *t* in [0, 0.5] and [bounceOut](#easeBounceOut) for *t* in [0.5, 1].
[ ](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceInOut)
](https://observablehq.com/@d3/easing#bounceInOut)